
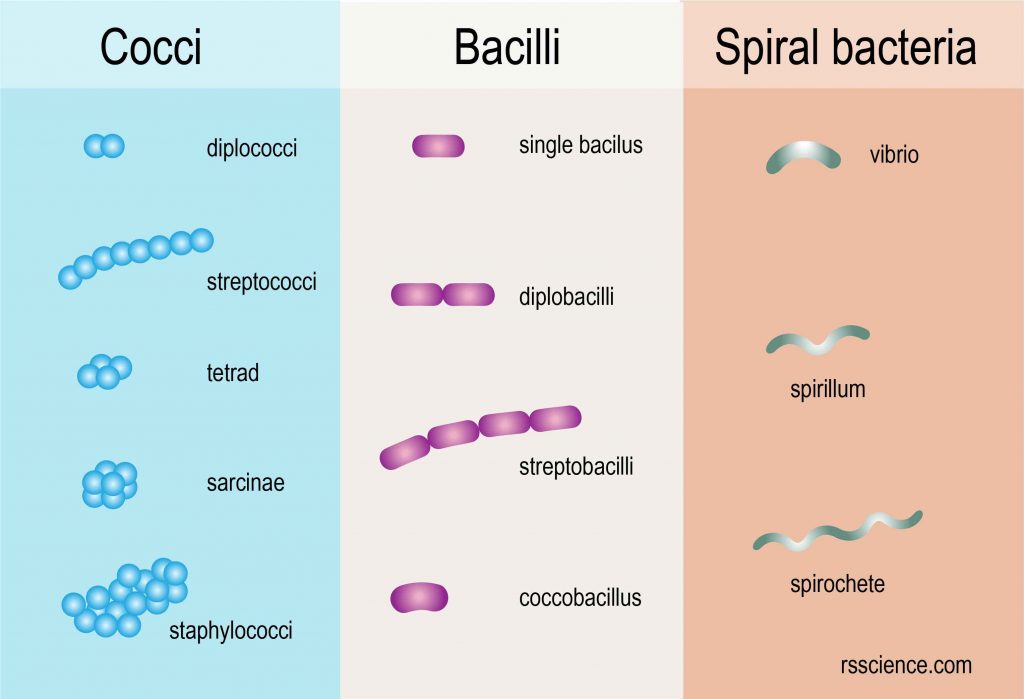
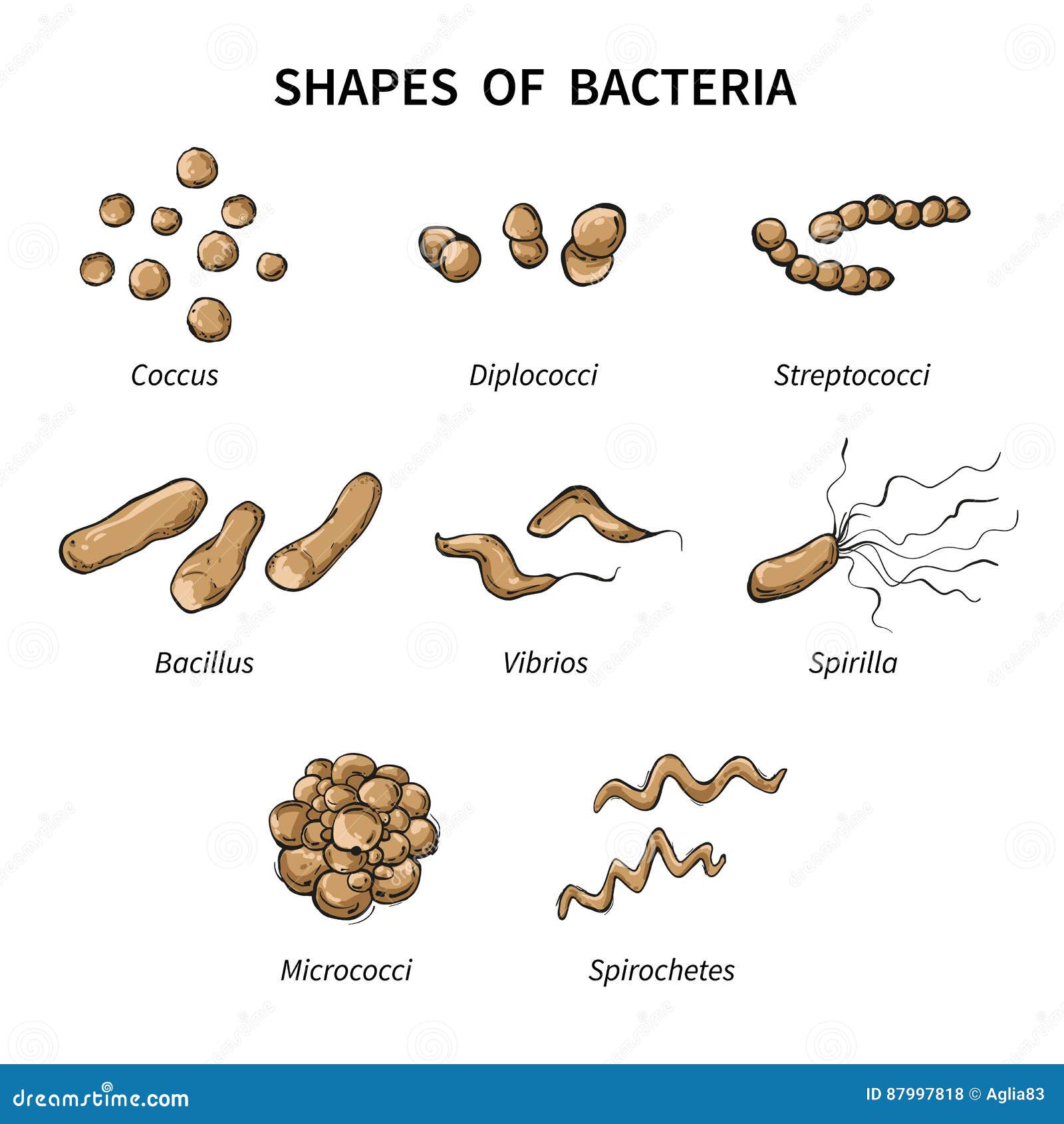
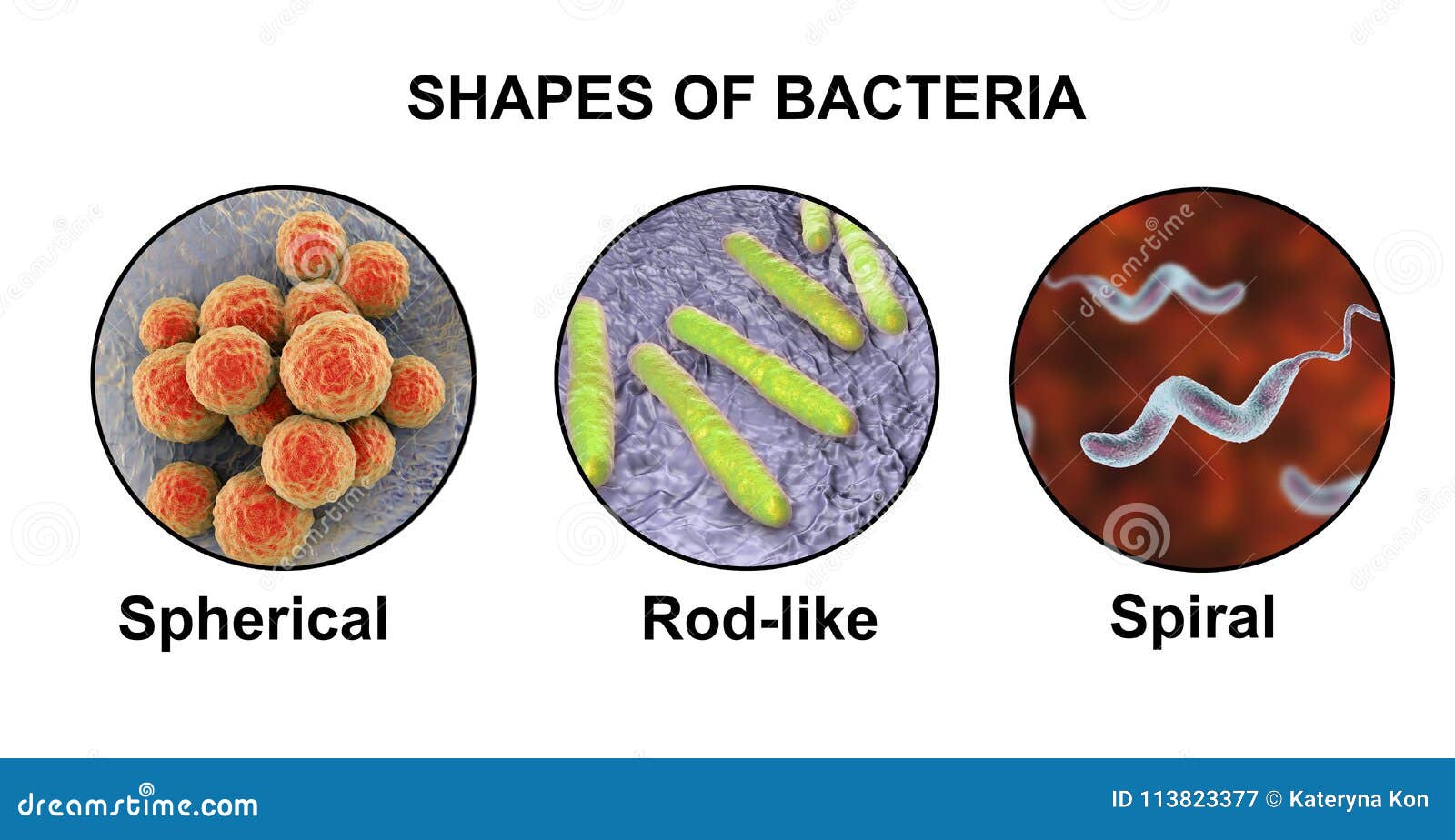
After that, they are again stained using a certain dye and then viewed with a light microscope. Some chemicals are first added to the bacteria-containing medium. The cell walls of bacteria are used for grouping bacteria into two major types. Some species of bacteria such as Streptococcus are protected from being eaten up (phagocytose) with the help of their cell walls.īacterial binding to the cell wall of the host is enabled with the help of its cell wall. The bacterial cell wall also serves as a barrier that prevents some toxic chemical and biological agents. It also protects the bacterial cell from bursting as a result of turgor pressure caused by osmosis this occurs when the bacteria is in a hypotonic environment. The bacterial cell protects it from any disruption caused by mechanical forces. The shape of bacteria is determined by its cell wall.
The capsules of bacteria also aid colonization by enhancing the attachment of bacteria cells to surfaces. Capsule-containing bacteria give rise to smooth, mucus-likeĬolonies when cultured compared to the unencapsulated bacteria that have nonmucoid colonies that are rough.īacterial capsules play protective roles by limiting their ingestion by white blood cells (leukocytes). This layer is called the Capsule when it is thick and firmly bound to the cell but referred to as a Slime layer when it is loosely bound and thinner. Many bacteria cells are surrounded by a thick layer made up of polysaccharides, polypeptides, or proteins that are hydrophilic in nature and gel-like. Processes such as protecting the bacterial cell against chemical and biological attacks in its environment while also aiding the colonization of surfaces by bacteria. The bacterial cell envelope carries out many cellular The envelope of the bacterial cell comprises complex structures that vary among different major groups of bacteria. The types of bacteria with their associated structures would be mentioned when discussing each structure below. Some bacteria cells have some structures that are not available in others. The structures listed above are not present in all types of bacteria.
Endospores – this consists of all bacteria cells components with dipicolinate and some special envelope components.Core components such as the cytosol, nucleoids, and plasmids.
Appendages which could be Pili or flagella.The Envelope, which consists of the bacteria cell wall, capsule, and cell membrane.Components that make up the structures of a bacterial cell Because the bacteria cell structure lacks a nuclear membrane, they are group as Prokaryotic cells different from the cells with nuclear membranes known as Eukaryotic cells. Hence the bacterial cell structure lacks a nucleus.
For the human cells, the nuclear materials are separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane known as the nuclear membrane. The genetic material of bacteria known as the nucleoid or nuclear body is not separated from the cytosol as in eukaryotic cells (such as that of human cells). The cytosol together with the nucleoid (also called the Nuclear body) forms the inner core of the general structure of bacteria cells. Most bacteria structures are made up of the envelope and its associated structures, the cytosol, and the nucleoid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
